Oracle Data Safe is Oracle’s platform for securing data in databases. As a native Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) service, Oracle Data Safe lets you assess the security of your database configurations, find your sensitive data, mask that data in non-production environments, discover the risks associated with database users, and monitor database activity.
Especially when you have an on-premises data centre, you need a safe and efficient way to manage the day-to-day security of your databases. You can use a secure TLS tunnel from databases to Oracle Cloud and use Oracle Data Safe as a unified control centre for your Oracle databases.
Architecture
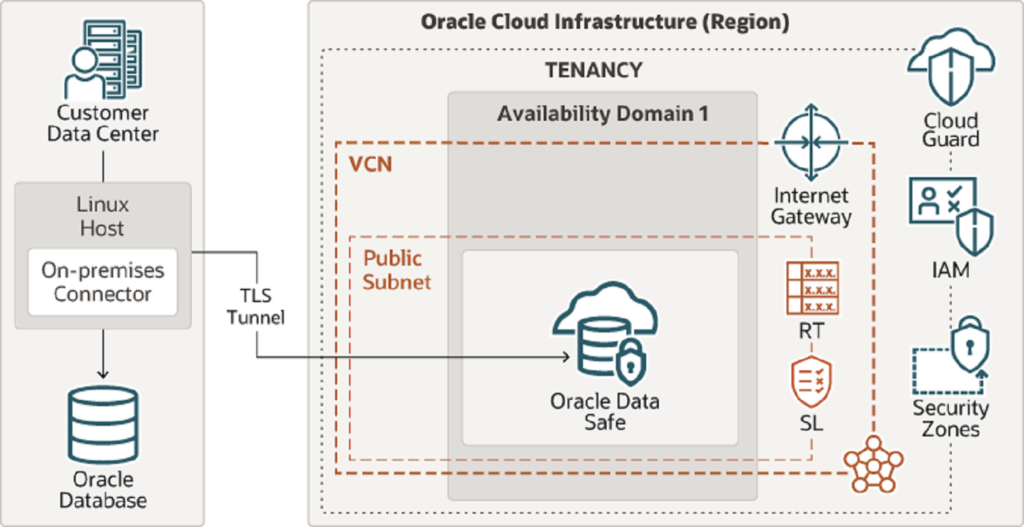
Oracle Data Safe is a unified control centre that monitors the day-to-day security of your Oracle Databases. The reference architecture illustrates a typical deployment of Oracle Data Safe using a secure TLS tunnel from on-premises to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). There are multiple options for establishing the connection between your databases and Oracle Data Safe, including using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect, VPN Connect, or using Data Safe’s on-premises connector. In most cases, if you don’t have FastConnect, then you should use the on-premises connector.
Components & Recommendations
-
Tenancy
A tenancy is a secure and isolated partition that Oracle sets up within Oracle Cloud when you sign up for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. You can create, organize, and administer your resources in Oracle Cloud within your tenancy.
When you subscribe to Oracle Data Safe, Oracle automatically creates a tenancy for you in OCI, if necessary.
-
Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centres, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
Oracle Data Safe can be enabled in the OCI Console. Oracle Data Safe must be enabled for each region in which it is intended to be used.
-
Oracle Data Safe
Oracle Data Safe is a unified control centre for your Oracle databases that is integrated into Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. It helps you understand the sensitivity of your data, evaluate risks to data, mask data, implement and monitor security controls, assess user security, monitor user activity, and address data security compliance requirements. Data Safe supports Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect, IPSec VPN, and On-Premise Connector to connect your on-premise location to the Oracle Cloud.
-
On-premises Connector
The on-premises connector is installed on a Linux host within the on-premises data centre and establishes a Transport Layer Security (TLS) connection between the Linux host and Oracle Data Safe. A TLS connection is a TCPS connection that uses a TLS cryptographic protocol. Oracle Data Safe’s on-premises connector supports version 1.2 of the TLS protocol and establishes the tunnel on port 443 (the standard HTTPS port). The on-premises connector can work through an HTTPS proxy server if desired.
-
Availability domains
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centres within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
-
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management (IAM) enables you to control who can access your resources in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and the operations that they can perform on those resources.
Oracle Data Safe uses all the shared services in OCI, including IAM. You can use the IAM service to set up user access to Oracle Data Safe.
-
FastConnect
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect provides an easy way to create a dedicated, private connection between your data centre and OCI. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect provides higher-bandwidth options, and a more reliable and consistent networking experience compared to internet-based connections. You should use FastConnect if it’s available.
-
VCN
When you create a VCN, determine the number of CIDR blocks required and the size of each block based on the number of resources that you plan to attach to subnets in the VCN. Use CIDR blocks that are within the standard private IP address space.
Select CIDR blocks that don’t overlap with any other network (in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, your on-premises data centre, or another cloud provider) to which you intend to set up private connections.
After you create a VCN, you can change, add, and remove its CIDR blocks.
When you design the subnets, consider your traffic flow and security requirements. Attach all the resources within a specific tier or role to the same subnet, which can serve as a security boundary.
-
Security lists
Use security lists to define ingress and egress rules that apply to the entire subnet.
-
Network security groups (NSGs)
You can use NSGs to define a set of ingress and egress rules that apply to specific VNICs. Oracle recommends using NSGs rather than security lists because NSGs enable you to separate the VCN’s subnet architecture from the security requirements of your application.
-
Cloud Guard
Clone and customize the default recipes provided by Oracle to create custom detector and responder recipes. These recipes enable you to specify what type of security violations generate a warning and what actions are allowed to be performed on them. For example, you might want to detect Object Storage buckets that have visibility set to public.
Apply Cloud Guard at the tenancy level to cover the broadest scope and to reduce the administrative burden of maintaining multiple configurations.
You can also use the Managed List feature to apply certain configurations to detectors.
-
Security Zones
For resources that require maximum security, Oracle recommends that you use security zones. A security zone is a compartment associated with an Oracle-defined recipe of security policies that are based on best practices. For example, the resources in a security zone must not be accessible from the public internet and they must be encrypted using customer-managed keys. When you create and update resources in a security zone, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure validates the operations against the policies in the security-zone recipe and denies operations that violate any of the policies.
-
HA/DR
In a production environment, Oracle recommends that you install the same on-premises connector on two Linux hosts for high availability. If one of your hosts goes down due to system failure or maintenance, Oracle Data Safe connections automatically fail over to the on-premises connector running on the other host, and ongoing Oracle Data Safe operations are not affected.
-
Security
Only open the specific ports to allow communication with the connection manager. You can control outgoing traffic from your host machine to the IP address of the cloud Connection Manager, which listens on port 443.
The address of a cloud Connection Manager is accesspoint.datasafe.REGIONNAME.oci.oraclecloud.com.
For example, for the Ashburn region, the address is accesspoint.datasafe.us-ashburn-1.oci.oraclecloud.com.
To obtain the IP address of the cloud Connection Manager, use DNS lookup.
In conclusion, Oracle Data Safe presents a comprehensive solution for fortifying the security of your on-prem databases, seamlessly integrated with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). By leveraging its advanced features, such as data discovery, vulnerability assessment, and user activity monitoring, businesses can ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their sensitive data.
If you need any help with your Application workloads on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), schedule a call with our OCI experts at Tangenz and we will contact you promptly.