In this article we will help you to understand the network connectivity options to integrate an application hosted in your local data center or third party data center. Architecture diagrams will help in understanding the technical and networking requirements for outbound and inbound communication from and to Oracle Utilities Cloud services.
Architecture
You can choose one of the following three architectures to integrate external applications with Oracle Utilities Cloud service.
Design 1: Integrating an external application with Oracle Utilities Cloud services through public (internet) web service APIs
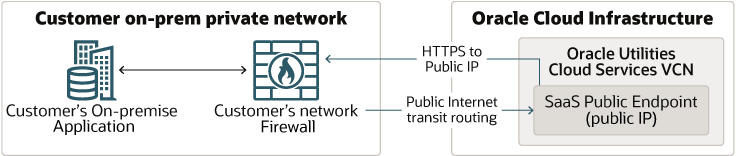
In this design – the external application and communicates to Oracle Utilities Cloud service over the public internet. The REST APIs on the Oracle Utilities Cloud services are exposed securely to the public internet, so if an on-premise application needs to access the REST APIs, it can do so, as long as the application has access to the public internet. Similarly, Oracle Utilities Cloud services can access web service end points that are exposed to the public internet (public IP) i.e., if the on-premise application’s web service end points are exposed to the public internet, then these can be consumed by Oracle Utilities Cloud services. A firewall in your corporate network may be configured to expose any application’s private end points to the public internet. Although this forms the simplest possible communication channel, transiting over the public internet requires close consideration of the security, availability and reliability that the public internet can provide.
Design 2: Integrating an external application with Oracle Utilities Cloud services through VPN Connect for private webservice APIs
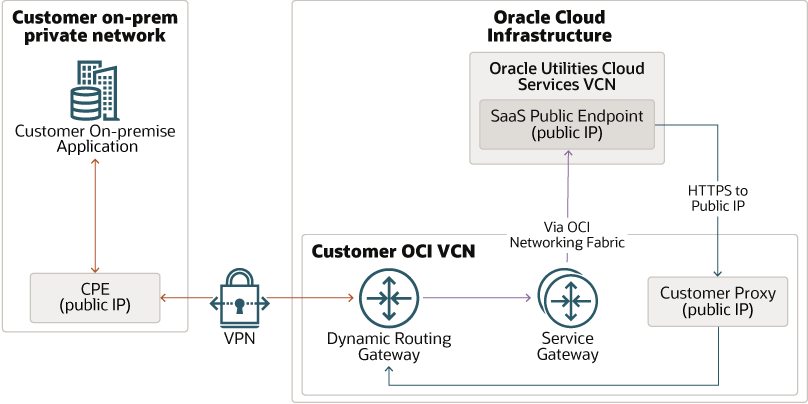
In this architecture, the external application makes private webservice API calls through the public internet, protected by an extended VPN, which creates a secured connection between your corporate private network and your VCN on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). Within OCI networking, communication between Oracle Utilities Cloud services’ VCN (Virtual Cloud Network) and your VCN uses the service gateway. VPN Connect requires setting up of CPE (Customer Premise Equipment), which interfaces with VPN DRG (Dynamic Routing Gateway) creating a IPSEC Encryption Tunnel over the internet, securing all information flowing through the tunnel. Authentication is provided by Oracle Identity Cloud Service. In turn, the Oracle Utilities Cloud service makes webservice calls to the external application by using Oracle Utilities Cloud service supported authentication methods such as basic authentication/OAuth client credentials, through the VPN. Note that Oracle Utilities Cloud services can make API calls only to public IP addresses, so you need to set up a proxy to expose your private API end points through public IP. The external application posts data to OCI object storage by using REST APIs. Note that Oracle Utilities Cloud services can make API calls only to public IP addresses, so you need to set up a proxy to expose your private API end points through public IP. The external application posts data to OCI object storage by using REST APIs. In the event that your external application’s digital certificates are not issued by a certification authority, you can use a single reverse proxy, with signed certificate, to proxy for multiple applications in your data center. The reverse proxy can be set up either in your data center or within your VCN in OCI.
Design 3: Integrating an external application with Oracle Utilities Cloud services through FastConnect for private webservice APIs
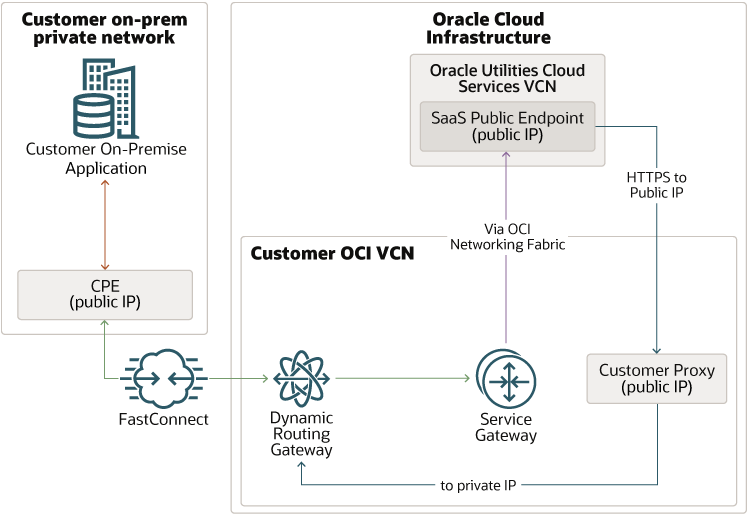
Alternately, another private routing option of FastConnect may also be used to connect your private/corporate network with OCI network(OCI VCN). FastConnect provides an entry point in to OCI for a dedicated private line between your data center and the OCI to enable high bandwidth data transfer over a highly secured channel. FastConnect communication requires FastConnect DRG to be setup on your OCI VCN along with a dedicated line that can connect the CPE with the FastConnect DRG to be set up, which in turn interfaces with the service gateway or the proxy within you VCN, depending on the direction of the communication. Within OCI networking, communication between Oracle Utilities Cloud Service’s VCN(Virtual Cloud Network) and your VCN uses the service gateway or your proxy depending on the direction of the API Call.
For all file based integrations, your on-premise application can post to or pulls from OCI object storage by using public(internet) REST APIs.
Networking Scenarios
Following four different networking scenarios can be described, based on the above three networking architectures, any of which you might consider when integrating Oracle Utilities Cloud Services with an application hosted externally.
Use the following table and associated topics to help you decide which networking option best fits your needs.
| Scenario | Description | Security | High Availability | Throughput | Cost |
| 1 | Connectivity over public internet without VPN or FastConnect | TLS only | Relies on connectivity over the internet | Limited | Low setup cost; Low setup cost; OCI data transfer charges may apply |
| 2 | Connectivity over public internet with VPN Connect and without FastConnect | IPSec, Encrypted | Limited | Typically <250Mbps | Low setup cost; Low setup cost; OCI data transfer charges may apply |
| 3 | Connectivity over FastConnect without VPN (VPN may reduce the throughput) | TLS over dedicated private line – Not Encrypted | Redundancy supported – Refer to High Redundancy Best Practices | Port speeds in 1 Gbps, 10 Gbps or 100 Gbps increments | Prominent setup cost; OCI data transfer charges do not apply |
| 4 | Connectivity over public internet with VPN (as a fallback) and FastConnect | Depending on the path used for communication (Fast Connect -Not Encrypted; VPN -Encrypted) | Redundancy by Design – Refer to Redundancy Best Practices | Depending on the path used for data transfer | Prominent setup cost; OCI data transfer fees may apply, depending on the path of communication |
Although connecting to Oracle Utilities Cloud Service via the internet is the cheaper option to setup, due to its limited security and availability, when transferring secured information as part of product integrations, it might also be the riskier option. Also, the OCI data transfer charges should be taken into consideration when evaluating the networking options. To ensure utmost security and availability, the FastConnect option with a redundant setup of VPN over public internet may be preferred.
Scenario 1: Connect Over Public Internet Without VPN or FastConnect
You can consider connecting over the public Internet without a VPN or FastConnect when the integration with on-premises application doesn’t need high bandwidth or high levels of security.
| Pre-requisites (To be done by the customer) |
|
| Working |
|
| Pros | Simple setup, lower cost. |
| Cons |
|
Scenario 2: Connect Over Public Internet With VPN but Without FastConnect
Connect over the public internet with a VPN Connect but without FastConnect when the integration with on-premises applications doesn’t need high bandwidth but needs higher levels of security, with private APIs for integration. Because FastConnect involves additional cost, you can use this scenario when cost is a factor but network throughput isn’t.
| Pre-requisite setup (To be planned and setup by the customer) |
|
| Working |
|
| Pros |
|
| Cons |
|
Scenario 3: Connect Over FastConnect Without VPN
Connect over FastConnect without a VPN when the integration with an on-premises application requires high bandwidth; for example, when you need to transfer large files.
| Prerequisites setup (to be planned and setup by the customer)s |
|
| Working |
|
| Pros | High bandwidth; secure line. |
| Cons | Cost of setting up the FastConnect private line and the cost of setting up the proxy and the service gateway. |
Scenario 4: Connect Over Public Internet with VPN and FASTConnect
Connect over the public internet with a VPN Connect and FASTConnect when the integration with an on-premises application requires not only high bandwidth, but also needs a fallback mechanism to ensure close to 100% availability. While the fallback mechanism in this case has a lower bandwidth, it ensures that connectivity persists.
| Pre-requisites: |
|
| Working: |
|
| Pros | High bandwidth, high availability, and secure. |
| Cons |
|
If you need any help with your Application workloads on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) , Please contact us here. Our OCI experts will contact you promptly.