Introduction
In this article, We will briefly discuss the possible ways to deploy/migrate Oracle E-Business Suite instance to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. Customers who want to provision a new Oracle E-Business Suite environment or migrate their existing E-Business suite to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) can leverage multi-host, secure and high-availability. Also oracle is providing automation to provision, migrate and manage the life cycle of Oracle E-Business Suite in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
Considerations
Oracle recommends to create separate subnets for each environment includes bastion host, database, application and load balancer instances to define appropriate security at different subnets.
Private and Public Subnets
You can create instances in either Private or Public subnets depending on the requirement from where you want to access through internet or local, Instances that are created in public subnet are assigned a public IP address and is used for internet access. You cannot assign a public IP address to instances created in private subnet and cannot be accessed publicly.
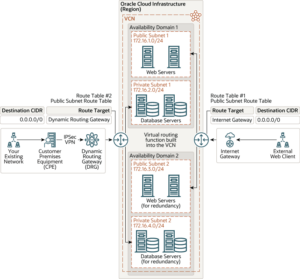
The following image shows a virtual cloud network (VCN) with public and private subnets. The VCN contains two availability domains, and each availability domain contains a public and private subnet. The web servers are placed in the public subnet in this image, so each web server instance has a public IP address attached to it. You can access these Oracle Cloud instances in the public subnet from the internet by enabling communication through the internet gateway (IGW). You’ll have to update the route table to enable traffic to and from the IGW. To permit traffic to the web servers from the internet, you must create load balancers in the public subnet. To access your instances from the internet, you also need to create a bastion host in the public subnet and access the bastion host from the IGW.
The database servers are placed in the private subnet in this image. You can access Oracle Cloud instances in the private subnet from your data centers by connecting through the dynamic routing gateway (DRG). The DRG connects your on-premise networks to your cloud network. To enable communication between the DRG and the customer on-premises equipment, use IPSec VPN or Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect. You’ll also have to update the route table to enable traffic to and from the DRG.
Scenario 1: Deploy All instances in Private Subnets
Oracle recommends this scenario for Production environments to avoid direct internet connection to instances. This scenario is suitable for hybrid deployment as an extension to your existing data centers.
To access these OCI hosted instances from your on-premise environments:
- Configure IPSec VPN between OCI and your data center using DRG (Dynamic Routing Gateway).
- Create bastion host and access all private subnet servers from bastion host.
Scenario 2: Deploy Instances in Public and Private Subnets
In this scenario few applications are deployed in a public subnet like iProc, iSupport etc and other applications are deployed in a private subnet like database, E-Business Suite Non-Internet applications.
Scenario 3: Deploy All Instances in Public Subnets
Oracle does not recommend this approach any Production Or Production equivalent environments. This scenario is best suitable for demonstrations and low critical applications.
Architecture
You can design your Oracle E-Business Suite deployment on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure in a single availability domain, across multiple availability domains, or in multiple regions. In addition, you can incorporate a demilitarized zone to isolate external traffic and protect internal systems.
Architecture for Deploying Oracle E-Business Suite in a Single Availability Domain
You can deploy Oracle E-Business Suite in a single availability domain and still ensure high availability by setting up multiple application instances. Use this architecture when you want to ensure that your application is available even when an application instance goes down. The other available application instances in the availability domain continue to process the requests.
The architecture consists of a virtual cloud network (VCN) with the bastion, load balancer, application, and database hosts placed in separate subnets of VCN in a single availability domain. In the following architecture diagram, the bastion host is deployed in a public subnet, and all the other instances are deployed in private subnets. You can place the different instances in public or private subnets based on your business requirements.
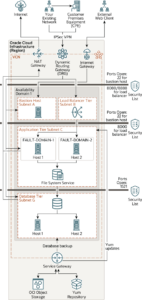
Architecture for Deploying Oracle E-Business Suite with a Demilitarized Zone (DMZ)
Use this architecture when you want your application to be accessible from external, untrusted networks while the internal systems are isolated from the external network.
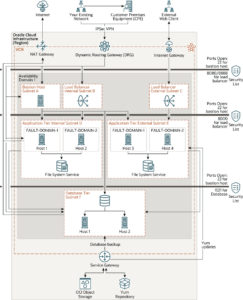
The architecture consists of a virtual cloud network (VCN) with the bastion host, an internal load balancer, an internal application tier, an external load balancer, an external application tier, and database hosts placed in separate subnets of VCN in a single availability domain. In the following architecture diagram, the external load balancer is deployed in a public subnet, and all the other instances are deployed in private subnets.
In this architecture, multiple application tier instances are deployed in a single availability domain, yet the individual application tier instances are placed in separate fault domains, allowing for high availability of the application tier. Fault domains enable you to distribute your instances so that they are not on the same physical hardware within a single availability domain. As a result, a hardware failure or hardware maintenance that affects one fault domain does not affect instances in other fault domains.
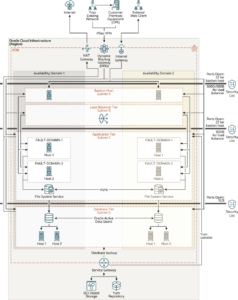
Architecture for Deploying Oracle E-Business Suite in Multiple Availability Domains
Use this architecture when you want to ensure that your application is available even when one availability domain goes down. You can still access the application instances in another availability domain.
This architecture shows the deployment of an Oracle E-Business Suite application across multiple availability domains. It shows a virtual cloud network (VCN) with the bastion, load balancer, application, and database instances placed in separate subnets across two availability domains.
Multiple application servers are deployed in each availability domain to ensure high availability within an availability domain. All application servers within an availability domain are deployed across different fault domains. By using different fault domains, application instances are protected against unexpected hardware failures and planned outages due to hardware maintenance. In addition, to ensure availability in case the primary availability domain is not available, redundant instances are created in another availability domain. In the architecture diagram, the instances in Availability Domain 1 are active and the instances in Availability Domain 2 are on standby. Oracle recommends that you set up application and database instances in symmetric topology across availability domains to ensure that your active instances serve the entire load when the primary availability domain is not available. In the symmetric topology, you deploy the same number of application and database instances on both the active and standby sites. When the instances in Availability Domain 1 are active, the load balancer is configured to direct traffic only to these active instances. The load balancer is not configured to direct traffic to the application server instances in Availability Domain 2. This means the application instances in Availability Domain 2 are not added to load balancer backend set. If Availability Domain 1 is not available, then you’ll have to manually switch over the application and database to the other availability domain. In this scenario, the application and database server instances in Availability Domain 2 become active. At this time, you need to update the backend set of the load balancer with application instances in Availability Domain 2 and also remove the application instances of Availability Domain 1. The load balancer will then accept requests and forward them to application servers in Availability Domain 2.
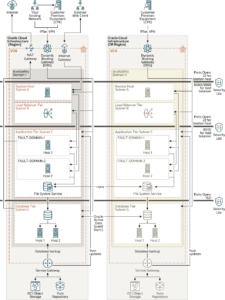
Architecture for Deploying Oracle E-Business Suite Across Multiple Regions
Use this architecture when you want to set up a disaster recovery site for your application in a different region. This architecture is essentially the same as the multiple availability domain architecture, but instead of creating resources in a second availability domain in the same region, you create resources in another region. In this architecture bastion, load balancer, application, and database instances are placed in separate subnets across multiple regions.
To ensure availability in case the primary region is not available, redundant instances are created in the standby region. The primary region contains active instances in an availability domain. The instances in an availability domain in the second region, called the disaster recovery region, are on standby. Oracle recommends that you set up application and database instances in symmetric topology across regions to ensure that your active instances serve the entire load when the primary region is not available. In the symmetric topology, you deploy the same number of application and database instances on both the primary and standby regions. In this architecture, multiple application servers are deployed in each availability domain to ensure high availability within an availability domain.
As this architecture is deployed in just one availability domain in region 1 and one availability domain in Region 2 for disaster recovery, it does not provide fault tolerance for availability domain in Region 1. If the only availability domain where application has been deployed is not available, you’ll need to invoke disaster recovery to fail over your application to Region 2.
If the instances in Region 1 aren’t available, then you must manually switch over to the instances in Region 2. For a seamless failover across regions, use logical host names for the Oracle E-Business Suite database and application instances. Use the same logical host names on the primary and standby sites to make it easier to failover or switch back without reconfiguring instances.
To replicate the database across multiple regions, use either Oracle Active Data Guard or Oracle Data Guard in asynchronous mode. To synchronize application servers across multiple regions, use rsync.
If you need any help with your Oracle EBS workloads on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) , Please contact us here. Our Oracle EBS and OCI experts will contact you promptly.